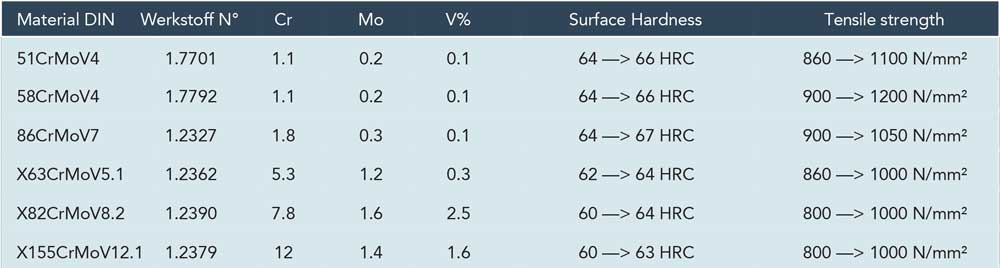
MATERIAL PROPERTIES
Influence of elements in steel chemistry
C:
Carbon is the most relevant element to control hardness charateristics, it is necessary to guarantee the correct martensitic tansformation.
Caution:
High C rate can lead to reduced toughness and is the principal cause of brittleness.
High C rate can give final undesired metallic structures leading to lack of wear resistance
High C rate is responsible of thermal shock sensibility and heating cracks propagation.
Cr:
Chromium carbides increase wear resistance, evenly increase the hardenability, break corrosion phenomena at high temperature, decarburization and oxides, increase mechanical characteristics at high temperature conditions, improve polishability.
Mo:
Molybdenum is responsible for steel hardenability, increases surface hardening depth because it decreases the critical cooling rate, guarantees uniformity for cross-section hardness, helps to keep small the austenitic grain during heating leading to fine martensitic structure.
V:
Vanadium is responsible for high yield strength and elongation and increases compressive strength, giving steel the best toughness and shock resistance cababilities; further increases wear resistance and helps to guarantee low grain size after hardening.
Ni:
Nickel increases the mechanical characteristic leading to high tensile strength meterials, slightly helps hardenability and increases impact strength.

CHROMIUM:

MOLYBDENUM: